
People often talk about cybersecurity- its importance and how your business should be prepared for a cyberattack. But are you aware of the different types of cyberattacks and what kind of threats they pose? Keep reading to learn more about the common types of attacks, the damage they can cause to your business, and how to prepare for and prevent them.
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyberattack describes unauthorized access or use of a device to steal or delete data, control or damage a device, or disrupt a service. Financial gains drive most attacks, but a small percentage of them are related to espionage.

Facts about Cyberattacks
According to a recent article from Varonis, 95% of data breaches are caused by human error, which means your employees could be putting your business at risk without even knowing it. Cybercriminals attack every 39 seconds, with $3.86 million being the average cost of an attack. Despite these facts, only 23% of organizations have an incident response plan in place. This means 77% of organizations are not prepared to handle the aftermath of a data breach.
Unfortunately, large businesses are not the only target of attacks. 43% of cyberattacks target small to medium-sized businesses, and 60% of small businesses do not survive a data breach. Don’t let your business fall into that category.
Types of Cyberattacks
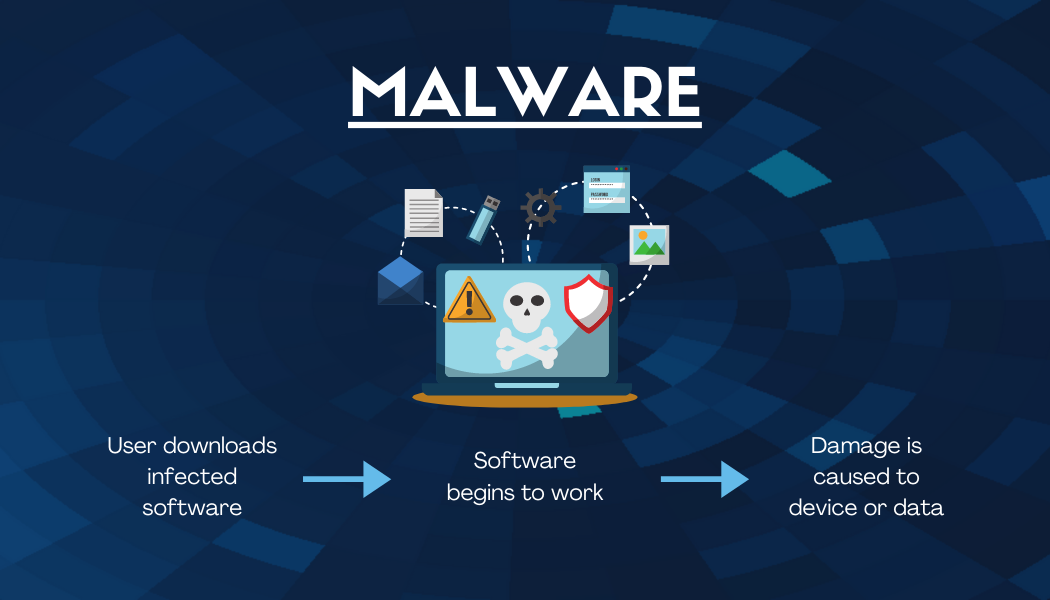
Malware
This type of cyberattack has four different methods: Ransomware, Spyware, Viruses, and Trojan Horses. These attacks occur when cybercriminals install malicious software on your device without your knowledge. Malware is used to gain access to information or damage the device.
Malware tricks users into clicking on or downloading infected software. The malware is often disguised in pop-ups claiming the user has won something or that the device is infected and instructs the user to click to run a scan or download anti-virus software. Once the user clicks, the malware is installed and obtains data or makes changes to the device. Ransomware, a type of malware, doesn’t just steal data or alter a device; it holds the device’s data hostage, demanding payment to unlock the device once it has been installed.
Though most malware is almost undetectable, there are a few ways to determine whether or not your device has been compromised. Do ads pop up immediately after a webpage loads, or do they appear even if you aren’t using your web browser? When you visit a webpage, are you re-directed through several different URLs? Are you unable to access your device control panel (only applicable for Windows systems)?
If you answered yes to one or more of these questions, chances are your device has been infected. If you believe your device has been infected, disconnect it from the internet and have your trusted IT specialist remove the infected software from your device.
Common ways to protect yourself and prevent malware from infecting your device include installing anti-virus software, enabling a firewall, and using strong passwords for your accounts. Protect your business by training employees to be suspicious of ads or links from untrusted sites or programs and emails requesting sensitive or confidential information.
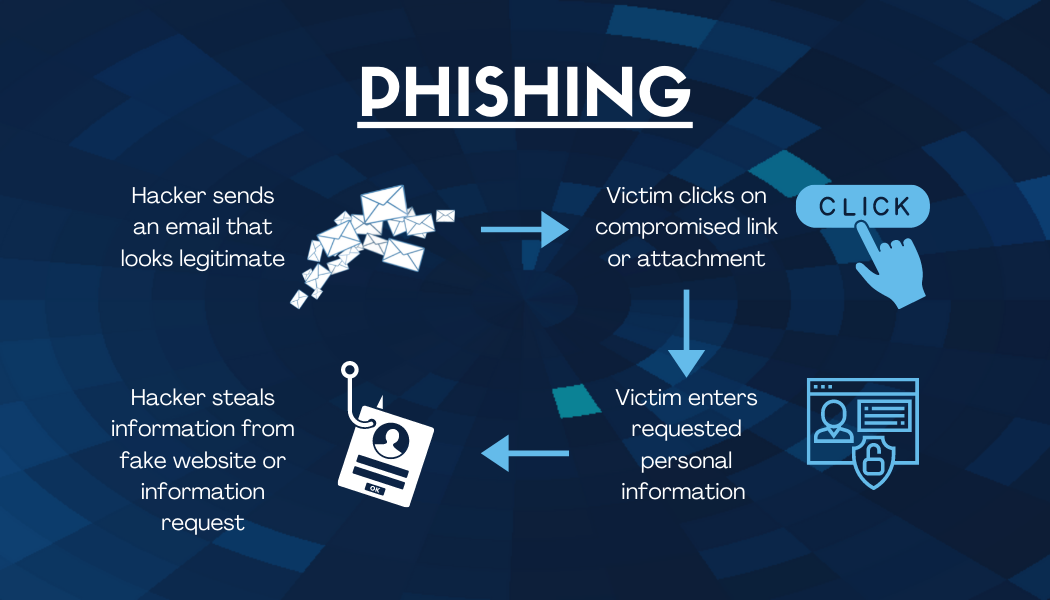
Phishing
This type of attack occurs through email. Cybercriminals will send emails with corrupted links or attachments disguised to look like they are from legitimate sources in hopes that the recipient will click on the link or open the attachment. By clicking on these links or opening the attachment, malicious software will deploy to access information or damage the device.
Another way phishing scams work is when the sender requests sensitive information from the recipient in hopes the recipient will respond with the information, which compromises the individual’s personal information or company data. Phishing scams have become increasingly sophisticated by replicating legitimate websites or disguising the sender’s information to look like the request came from a trusted source.
So, how do you protect yourself from this type of cyberattack? Always be suspicious of emails from unknown senders or emails containing only a link or attachment from known senders.
Did you receive an email from a site or service that you didn’t subscribe to? Or an email with a discount or coupon link from a business that you haven’t purchased from recently? Or perhaps you received a request for information from a trusted source, but the body of the email doesn’t sound like it was sent from them. All of these are signs of phishing. Train your employees to be on the lookout for emails that don’t seem legitimate. Instruct them not to open emails from unknown senders and to avoid clicking on links or attachments that seem suspicious.
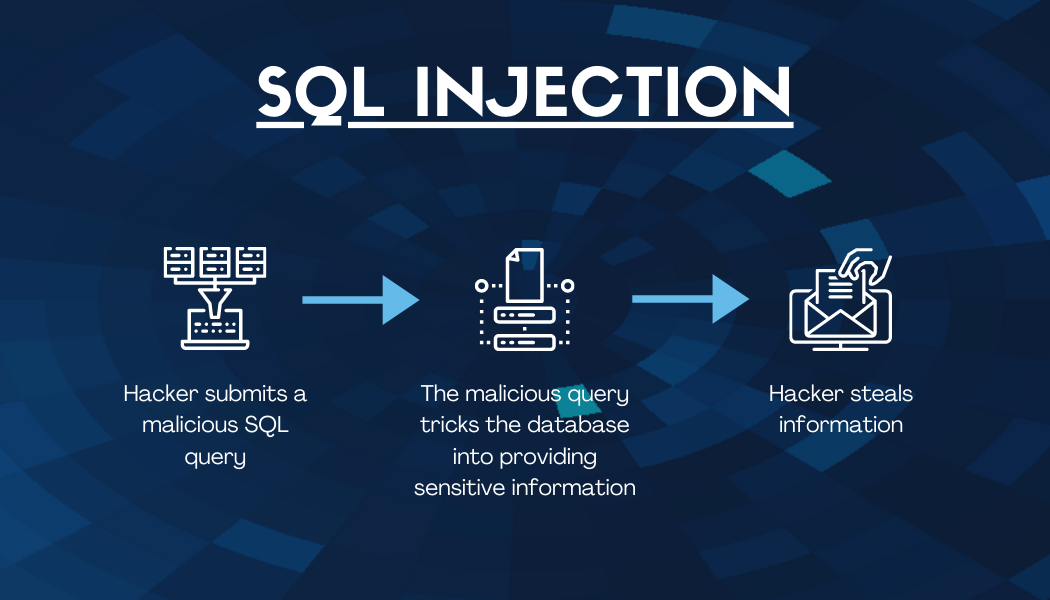
SQL Injections
These attacks are focused on data-driven applications where a malicious line of code is inserted into a field, allowing sensitive information to become visible to the attacker. Data obtained can range from company data to client lists, personal information, and more.
The best way to protect your business from this type of attack is to close as many security gaps upfront by setting limits on returned results, eliminating freeform input as much as possible, validating and cleansing data before processing, and performing tests to expose areas of vulnerability. On top of that, limit database access to only those that need it and complete regular backups.
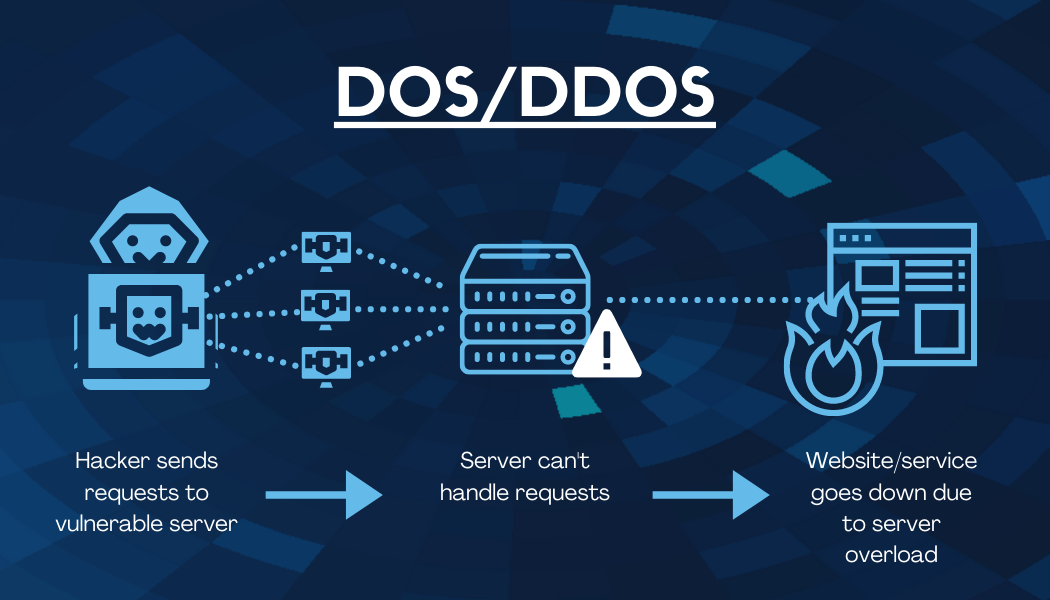
DoS or DDoS (denial of service, distributed denial of service)
A denial of service (DoS) or distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is where the attacker disrupts a service by overwhelming the server with requests. The difference between a DoS and a DDoS attack is that a DDoS attack comes from multiple sources at once, whereas a DoS attack only comes from one source. This type of attack disrupts a service by causing a system to crash or forcing a website offline.
So how do you protect your business from this type of attack? The best course of action is creating and developing a specific response plan for a DoS or DDoS attack. Minimize attack risk and mitigate this type of security threat by updating your systems and software regularly. Outdated systems and software pose the greatest risk for a DoS or DDoS attack because there are more security holes. You should also utilize a strong firewall, VPN, and anti-spam to further your protection.
Cloud-based solutions are ideal for small to medium-sized businesses because they offer advanced DDoS mitigation at a reasonable cost. The cloud is also more effective at absorbing the traffic from an attempted attack before reaching the intended target.
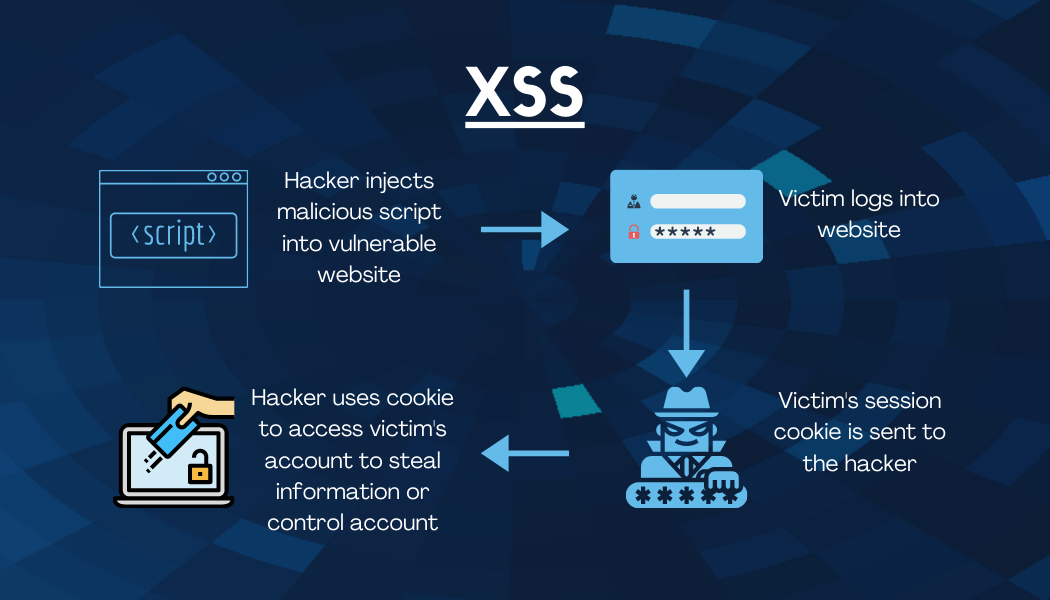
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
This type of attack exploits website application vulnerabilities, allowing the attacker to steal cookies to gain user or admin access to a website. They then can steal any saved information under the accounts, such as personal information or credit cards. The attacker can change the user or admin’s login information to keep access to the account. This type of attack works when malicious code is injected on the user side through a website, link, message board, forum, or other ways where comments are allowed.
Prevent an XSS attack by sanitizing and filtering your input. This means input data is not directly distributed to the browser before it is checked for malicious code and automatically filters out dangerous keywords.
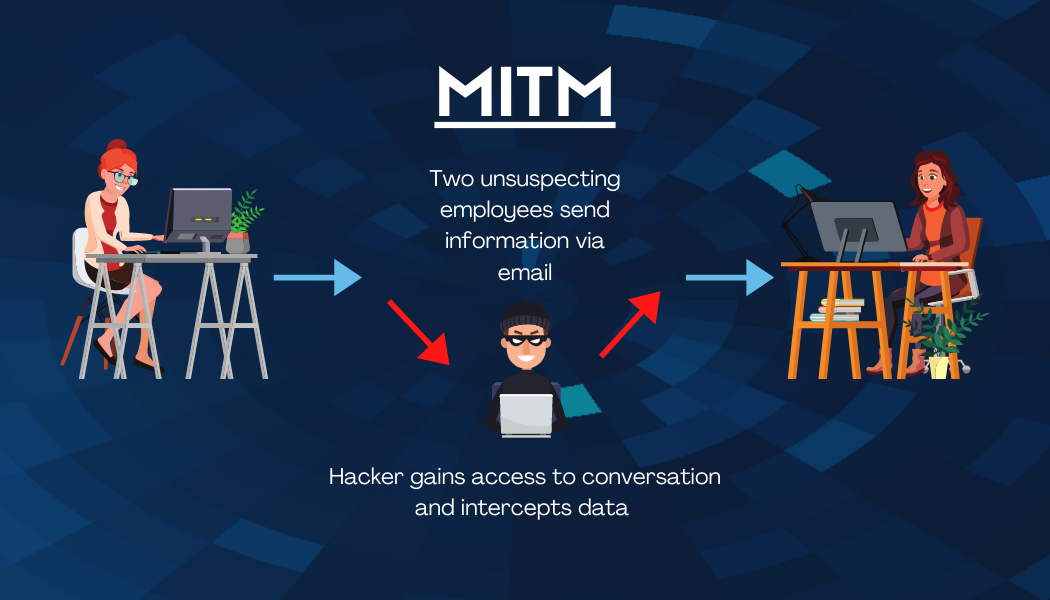
MitM Attack (Man in the Middle)
A man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack is where the attacker secretly gains access to a conversation between two parties. The attacker then intercepts all data sent between both parties. A MitM attack can occur even if you are sending and receiving data from a trusted source. Types of MitM attacks include IP spoofing, Email hijacking, HTTPS spoofing, and eavesdropping.
One of the best ways to prevent MitM attacks is to avoid using public Wifi when possible. Opt for your mobile data or your mobile hotspot instead. This is not the only option and won’t always protect you, however. You can protect yourself and your business by using a VPN and two-factor authentication and only visiting HTTPS websites.

Password Theft
In 2020, 81% of data breaches were caused by compromised login information. Passwords are stolen through various tactics such as phishing and MitM. Password theft also occurs in large-scale data breaches from companies that you have accounts with.
How do you protect your business from password theft when it’s not always in your control? A few of the easiest ways to reduce the risk of password theft are using long, random, strong passwords, using different ones for each account, and never sharing passwords. Another way to protect yourself is by using two-factor authentication or biometrics if it is an option. Lastly, you can use a password manager to manage your login information.
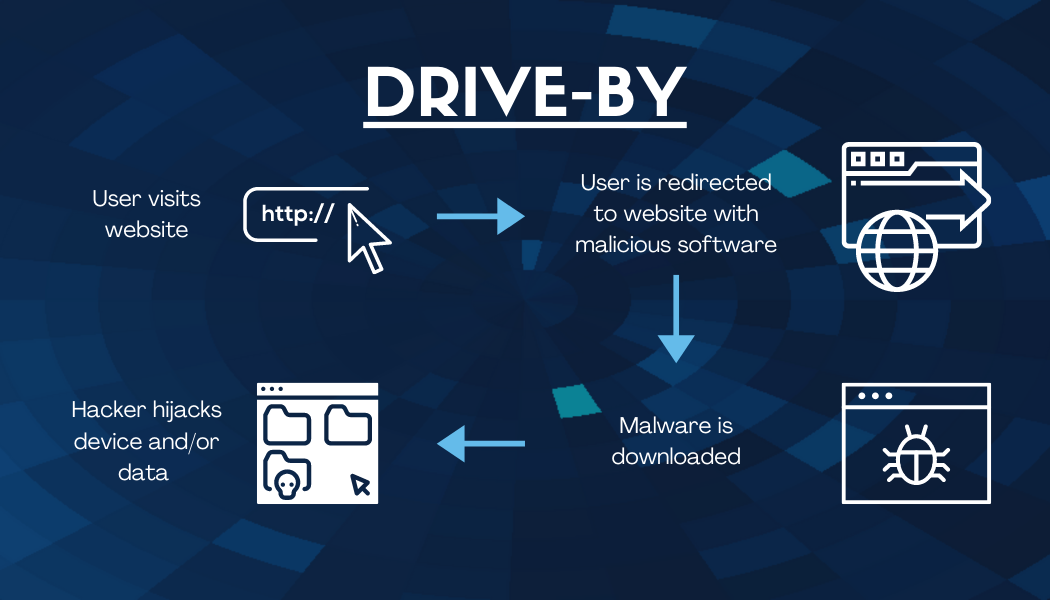
Drive-By Attack
These attacks prey on visitors of compromised websites or apps that instruct the unsuspecting user to download malware. The malware then infects the user’s device, which compromises either or both the device or data. The goal of these attacks is to steal data, hijack the data or device, destroy or damage the data or device, or spy on the victim of the attack.
If these attacks are random, then how can you protect yourself and your employees? By updating your devices and software regularly and installing protective software on those devices, properly training your employees to avoid suspicious websites, links, or files, and deploying software that blocks suspicious or malicious websites.

Zero-Day Exploit/Attack
This type of attack is very dangerous because only the attacker is aware of the vulnerability. They exploit it using malware such as a worm or virus to access information or damage a device. The name comes from the number of days a developer has been aware of the vulnerability, which is zero. These vulnerabilities are fixed with what is called a software patch.
Preventative security measures are the best way to avoid this type of attack from happening. These measures include maintaining a strong, up-to-date firewall and anti-virus software. Completing regular data backups is not necessarily a preventative measure, but it is a way to ensure your downtime and cost incurred is as minimal as possible.

This is not a complete list of all the types of cyberattacks that can happen, but they are the most common that occur each year. If you’re not sure how to protect your business from cyberattacks and data breaches, contact our team of IT professionals today to discuss how we can help keep your business safe and secure.